LED Screen Brightness Secrets Everyone Should Know
- Home
- »
- LED Display Technology
- »
- LED Screen Brightness Secrets Everyone Should Know
Table of Contents
LED screen brightness determines the clarity, visibility, and overall viewing experience of LED displays. Proper luminance ensures content remains readable in diverse environments, from indoor classrooms to bright outdoor advertising walls. Users often face challenges such as glare, dim spots, or uneven brightness, making it essential to understand recommended brightness levels, measurement methods, and maintenance practices. This guide explores all aspects of LED screen brightness, from technical considerations and practical selection tips to future developments like MicroLED and intelligent brightness management, helping users make informed decisions for any application.
1. What Is LED Screen Brightness?

LED screen brightness measures the luminance a display emits, in nits (cd/m²) — the light output per square meter. This differs from lumens, which describe total light output rather than how bright a screen appears to viewers. For example, a 3000-nit display emits 3000 candelas per square meter, directly influencing visibility and color clarity under different lighting conditions. To avoid making a costly mistake, it’s critical to understand the difference of Nits vs. Lumens.
Users often wonder how bright an LED screen needs to be for daytime readability or whether a screen will remain clear under direct sunlight. These questions reflect real-world concerns: in bright outdoor areas, a standard indoor-level brightness can appear dim, while overly bright screens indoors may cause glare and eye fatigue. Semi-outdoor spaces, such as shop windows or transit areas, present another challenge, where the screen must adapt to shifting light throughout the day — requiring a high bright LED screen to maintain legibility without discomfort.
Brightness selection also depends on screen size and viewing distance. Large LED walls used for concerts or advertising must have sufficient luminance to ensure that images remain sharp even for viewers at a distance, which is why users researching how bright are LED screen walls pay close attention to nits ratings. Similarly, consumer concerns like LG LED TV bright spots on screen often stem from uneven LED aging or backlight issues, highlighting that consistent and sufficient brightness is essential for both professional and home displays.
2. Recommended Brightness Levels for Different Applications
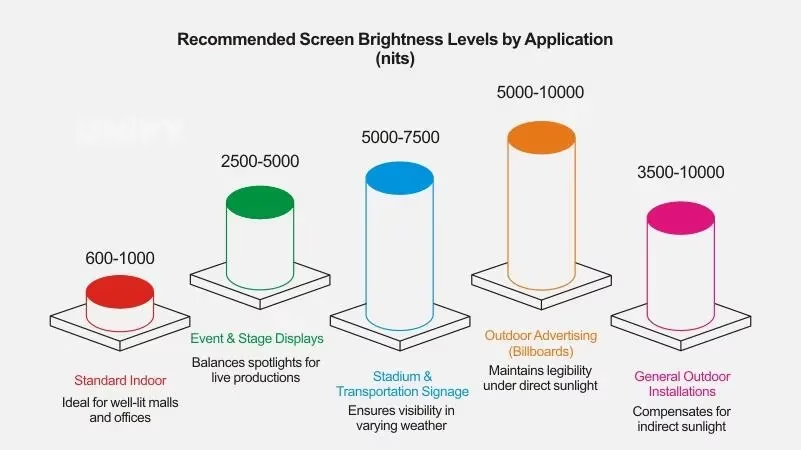
Choosing the right LED screen brightness depends on the environment, viewing distance, and screen size. Users often wonder how bright a display needs to be for indoor spaces, semi-outdoor areas, or large outdoor events, because improper brightness can lead to poor visibility, glare, or unreadable content.
Indoor LED Screens (600–1,500 nits)
For indoor LED screen environments such as conference rooms, retail stores, or classrooms, a brightness range of 600–1,500 nits is typically sufficient. Screens in this range provide clear images while minimizing glare and eye fatigue, which are common user concerns. Excessive brightness indoors can cause discomfort, while too low brightness reduces legibility across the room.
Semi-Outdoor or Bright Indoor Spaces (2,000–4,000 nits)
Areas exposed to strong natural light, including shopping malls, exhibition halls, or transit stations with large windows, often require 2,000–4,000 nits. A high bright LED screen ensures content remains legible even under direct sunlight or bright daylight reflections. Users frequently report that standard indoor screens appear washed out in these environments, highlighting the need to match brightness to ambient light conditions. In regions with intense sunlight, such as Southeast Asia or southern US states, leaning toward the upper end of this range is advisable.
Outdoor Advertising, Stadiums, and Large Events (5,000–10,000+ nits)
Outdoor LED screen applications, including billboards, stadium displays, and daytime event screens, demand 5,000–10,000+ nits to maintain visibility in direct sunlight. Large LED walls must provide sufficient luminance to remain sharp and readable for audiences at a distance, which is why professionals assessing how bright are LED screen walls focus closely on nits ratings. In tropical or desert climates, brightness requirements often exceed 6,000 nits to combat strong sunlight and reflections.
While 6000 nits ensures visibility under sunlight, it also requires more energy. To learn how to estimate your running costs, check our guide on LED display power consumption.
Technical Considerations
Screen size and viewing distance: Larger screens or distant viewers require higher brightness to maintain clarity.
Content type: Text-heavy displays need slightly higher brightness than image-based content for readability.
Light fluctuations: Semi-outdoor and outdoor screens should account for changing sunlight throughout the day.
Verification: Users can measure brightness using a light meter or spectrometer at multiple points to ensure the display meets specifications and provides uniform luminance.
By selecting the appropriate brightness based on application, environment, and user needs, LED displays can achieve optimal visibility, comfort, and impact across different scenarios.
While standard LCD panels typically max out around 700 nits, they often appear washed out in direct sunlight. For a deeper look at how this impacts visibility, read our full comparison on LCD vs LED brightness.
3. Measuring and Verifying LED Screen Brightness
Accurately determining LED screen brightness is essential to ensure that a display performs as expected. Users often want to verify LED screen manufacturer claims, because discrepancies in brightness can lead to poor visibility, uneven images, or wasted energy.
Tools for Measurement
Brightness is commonly measured using a light meter or a spectrometer. A light meter provides quick on-site readings of luminance in nits (cd/m²), while a spectrometer can measure brightness and color accuracy simultaneously, ensuring that both clarity and visual fidelity meet expectations.

Measurement Methods
Multi-point measurements: Checking multiple points across the screen helps identify uneven brightness or hot spots, which are common issues in large LED walls.
Standardized environment: Measuring under controlled lighting conditions reduces interference from ambient light and allows comparison with manufacturer specifications.
Repeat checks: Periodic measurements over time can detect brightness drift due to LED aging or heat accumulation, especially for screens exposed to long hours of operation.
Many users notice that rated brightness does not always match perceived brightness. For instance, a screen rated at 5,000 nits may appear dim if certain modules are misaligned, aged, or improperly calibrated. Multi-point measurements and standardized testing help confirm that LED screen brightness is consistent and sufficient for the intended environment, ensuring readability and uniform image quality for all viewers.
4. Key Factors Affecting LED Screen Brightness
The brightness of an LED screen is determined by several technical factors that influence visibility, image clarity, and long-term performance. Users frequently ask why a screen may appear dimmer than expected, why brightness varies across the display, or why outdoor screens sometimes fail to maintain clarity. Understanding these factors helps select and maintain the right display.
Ambient Light Intensity
The surrounding light environment is a primary determinant of perceived brightness.
Indoor applications: 600–1,500 nits typically provide clear images without glare.
Outdoor or direct sunlight: Screens often require 5,000–10,000+ nits to remain legible.
Users often report that indoor-rated screens appear washed out in bright semi-outdoor areas, emphasizing the importance of matching brightness to ambient light.
Pixel Density, LED Packaging, and Driving Current
Pixel density affects detail; higher density can reduce perceived brightness if LEDs are small or tightly spaced.
LED packaging and driving current directly impact luminance. Typical high-brightness LEDs operate at currents that allow 2,000–5,000 nits per module.
Dim spots on a screen often result from insufficient current, low-efficiency LEDs, or suboptimal packaging. Understanding these technical parameters helps users identify performance limitations.
Screen Structure and Heat Dissipation
The physical design of the panel and thermal management affects brightness stability. Poor heat dissipation can cause LEDs to dim, particularly in high bright LED screens running for extended periods. Users may notice brightness reduction during long operations if panels lack adequate cooling.
Aging and Usage Time
LEDs degrade over time, reducing maximum brightness and causing uneven luminance. Large LED walls in continuous operation can lose 10–20% of initial brightness after several thousand hours. Users concerned about bright LED screen uniformity often experience this effect. Regular monitoring and module replacement help maintain consistent performance.
Key factors — ambient light, pixel density, LED type and driving current, panel structure, and aging — all influence LED screen brightness. By understanding these elements, users can select appropriate screens, ensure uniform image quality, and maintain optimal visibility for indoor, semi-outdoor, and outdoor applications.
5. LED Screen Brightness Uniformity and Color Perception
Achieving the correct LED screen brightness involves more than reaching a high nits value. Uniformity and color perception are critical for delivering a consistent and comfortable viewing experience. Users frequently notice dim spots, uneven luminance, or washed-out images on large LED walls, raising concerns about visual quality.
Brightness Uniformity
Uniform brightness ensures all areas of a screen display content evenly. Variations can result from differences in LED modules, aging, or thermal effects.
Typical uniformity target: 90–95% across the panel.
Multi-point measurement, as discussed in Chapter 3, can detect hot spots or dim areas.
Maintaining uniformity is essential for high brightness LED screens in advertising, events, or control rooms, where small discrepancies are noticeable to viewers.
Color Temperature and Its Effect on Perceived Brightness
Color temperature affects how bright a screen appears.
Cool tones (6,500K–7,500K) often appear brighter than warm tones (3,000K–4,500K) at the same nits rating.
Users adjusting text or image visibility often perceive brightness differences even when measured luminance remains constant.
Gray Scale Calibration
Proper gray scale calibration improves both color accuracy and perceived brightness.
Smooth gradations between black and white prevent visual banding.
Enhances overall uniformity, making content appear brighter and more vivid.
Typical calibration involves adjusting 16–256 gray levels depending on screen type and pixel pitch.
Maintenance and Best Practices
Regular calibration and monitoring can maintain brightness uniformity over time.
Thermal management and module inspection prevent hot spots and dimming.
Users can combine multi-point brightness measurements with color calibration to ensure optimal visual performance.
Consistent LED screen brightness depends not only on nits but also on uniformity, color temperature, and gray scale calibration. By applying proper calibration, monitoring aging, and addressing thermal effects, users can achieve clear, even, and visually comfortable displays across all viewing conditions.
6. Choosing the Right Brightness for LED Screen
Selecting the appropriate LED screen brightness is critical for visibility, visual comfort, and energy efficiency. Users often ask how to determine the correct brightness for different environments, screen sizes, or content types. This guide combines technical considerations with practical tips to help make informed decisions.
Assess Ambient Light Conditions
The surrounding light significantly affects perceived brightness.
Indoor environments: 600–1,500 nits are generally sufficient.
Semi-outdoor or bright indoor spaces: 2,000–4,000 nits help maintain clarity.
Outdoor or direct sunlight: 5,000–10,000+ nits are recommended for large displays.
Considering ambient light prevents issues like washed-out images or excessive glare, common user concerns.
Evaluate Viewing Distance and Screen Size
Larger screens or distant viewers require higher brightness to maintain readability.
Short viewing distances allow moderate brightness without loss of detail.
For high bright LED screens, longer viewing distances demand higher nits to ensure all viewers see content clearly.
Consider Content Type
Different content types have varying brightness requirements:
Text-heavy content: Needs higher brightness for sharp readability.
Images or videos: Moderate brightness with proper color calibration can enhance visual quality without causing eye fatigue.
Factor in Energy Efficiency and Lifespan
Higher brightness increases power consumption and accelerates LED aging.
Users often ask how to balance brightness, energy costs, and screen longevity.
Choosing screens with automatic or manual brightness adjustment can optimize performance while conserving energy.
Compare Specifications with Real Visual Performance
Manufacturer specifications provide a reference, but real-world performance may differ due to panel quality, calibration, and environment.
Verify brightness using multi-point measurements (see Chapter 3) and visual inspection.
Ensures that a high bright LED screen truly meets the required luminance for its application.
Choosing the right LED screen brightness requires considering ambient light, screen size, viewing distance, content type, energy efficiency, and real-world performance. By evaluating these factors, users can achieve optimal readability, visual comfort, and long-term reliability, whether for indoor installations, semi-outdoor spaces, or large outdoor displays.
7. Optimizing and Maintaining LED Screen Brightness
Maintaining optimal LED screen brightness ensures consistent visual quality, readability, and long-term durability. Users often notice dim spots, uneven luminance, or color shifts after extended use, highlighting the importance of systematic optimization and maintenance.
Automatic Brightness Control and Ambient Light Sensing
Modern LED screens often include automatic brightness adjustment based on ambient light sensors:
Function: Adjusts brightness in real time to maintain visibility under changing light conditions.
Benefit: Reduces power consumption and prevents excessive LED wear, addressing common user concerns about energy costs and screen longevity.
Practical tip: Check sensor calibration every 6–12 months to ensure consistent performance.
Regular Cleaning and Heat Management
Dust, dirt, or poor ventilation can reduce perceived brightness and accelerate LED aging:
Cleaning frequency: Light surface cleaning monthly; deep cleaning and inspection every 6 months.
Heat management: Ensure proper airflow and verify cooling systems to prevent hotspots that cause dimming.
Users have reported brightness drops of 5–15% when maintenance was neglected for more than a year.
Color and Gray Scale Calibration
Calibration ensures uniform brightness and accurate color reproduction:
Gray scale levels: Adjust 16–256 levels depending on screen type.
Frequency: Every 3–6 months or after major content changes.
Proper calibration corrects visual inconsistencies caused by LED aging or environmental factors and improves perceived luminance.
Monitoring LED Aging and Module Replacement
LEDs gradually lose brightness over time due to continuous operation and thermal stress:
Monitoring: Conduct multi-point brightness measurements quarterly.
Replacement: Modules should be replaced when brightness drops more than 10% compared to new modules.
Regular monitoring ensures consistent luminance and prevents uneven brightness across large LED walls.
Optimizing and maintaining LED screen brightness involves automatic controls, scheduled cleaning, thermal management, gray scale calibration, and module monitoring. Following these practices maintains clear, uniform, and visually comfortable displays over the operational lifespan, addressing common user concerns about dimming, uneven images, and long-term durability.
8. Risks of Too High or Too Low Brightness
Incorrect LED screen brightness settings can lead to visual discomfort, display issues, and reduced LED lifespan. Focusing on the risks rather than maintenance helps users understand potential consequences and make informed decisions.
Risks of Too Low Brightness
When brightness is too low, content may become difficult to see, especially in bright environments. Text, images, and videos can appear washed out or lack contrast, reducing readability and viewer engagement. This is particularly noticeable on indoor or semi-outdoor screens where ambient light varies throughout the day.
Risks of Too High Brightness
Excessive brightness can cause glare, making viewing uncomfortable and leading to eye fatigue during prolonged exposure. High luminance also increases energy consumption and accelerates LED aging. Users have reported cases like LG LED TV bright spots on screen, which occur when LEDs are overdriven or unevenly aged, highlighting the importance of monitoring extreme brightness levels.
Maintaining balanced LED screen brightness is essential for clarity, visual comfort, and hardware longevity. Too low brightness can make content hard to read, while too high brightness can cause glare, eye fatigue, and uneven LED wear. Understanding these risks allows users to set safe and effective brightness levels for various environments and content types. Regular monitoring helps detect potential issues early, ensuring consistent and reliable display performance, including for high brightness LED screens.
9. How Bright Should LED Screen Walls Be for Advertising and Events?
Large-scale LED walls are widely used for outdoor advertising, stadiums, and live events, where brightness is critical for visibility and viewer engagement. Users often ask how bright these screens need to be to ensure content is clear, legible, and visually impactful under different lighting conditions.
Brightness Impact on Large LED Walls
High brightness ensures content remains visible from a distance and under varying lighting conditions. On large displays, uneven luminance or color shifts are more noticeable, which can distract viewers and reduce the impact of advertisements or event visuals. Users often report that sections of a large screen appear dimmer or display subtle bright spots, highlighting the importance of proper calibration and uniformity.
Key Considerations for Large Screens
Viewing distance affects how brightness is perceived across the entire screen. Ambient light conditions, such as direct sunlight or bright indoor environments, influence visibility. Content type also matters—text-heavy content requires consistent luminance for readability, while video content benefits from controlled peak brightness to avoid glare. Regular calibration ensures high brightness LED screens maintain uniformity and color accuracy across all sections.
Determining how bright LED screen walls should be goes beyond raw nits—it requires balancing visibility, uniformity, and viewer comfort. Considering factors such as viewing distance, ambient light, content type, and calibration ensures that large LED walls deliver clear, consistent, and engaging visuals for advertising and events, while minimizing issues like uneven brightness or color shifts.
10. Future Developments in LED Screen Brightness
The evolution of LED screen brightness is shaping the next generation of displays, focusing on higher luminance, smarter management, and energy efficiency. Users and professionals are increasingly interested in how future technologies can improve visibility, color consistency, and overall viewing experience.
MicroLED and Enhanced Brightness Performance
MicroLED technology offers significant improvements in brightness, achieving higher luminance without compromising color accuracy or contrast. For users, this means clearer content under bright environments such as outdoor advertising or large event screens. The uniformity and peak brightness of MicroLED displays also reduce common issues like uneven luminance, enhancing viewer comfort.
Intelligent Brightness Management
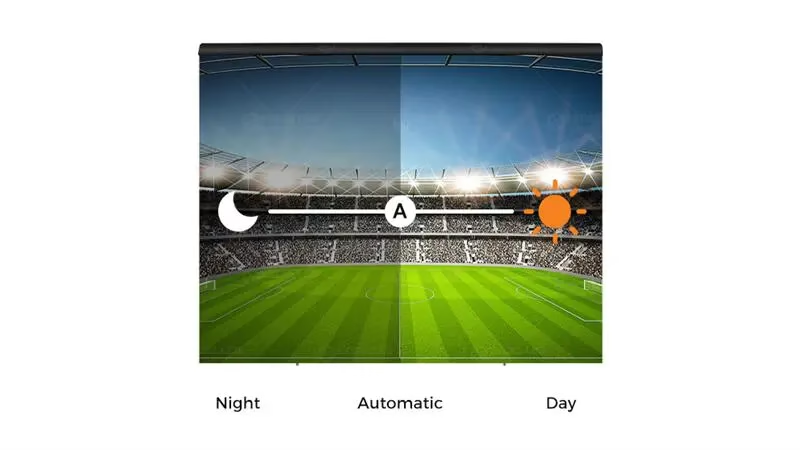
Future high brightness displays incorporate smart brightness management. Automatic adjustments based on ambient light ensure optimal visibility in varying lighting conditions, from indoor events to direct sunlight outdoors. This technology addresses user concerns about glare, readability, and energy consumption while maintaining consistent LED screen brightness.
Automated Brightness Adjustment and Energy Efficiency
Advancements in automated brightness control and energy-efficient LED driving circuits allow screens to maintain desired luminance while reducing power usage. Users benefit from displays that stay bright and uniform over time, with less maintenance required. These developments also extend the operational lifespan of high brightness LED screens and improve viewing comfort.
The future of LED screen brightness focuses on maximizing visibility, consistency, and energy efficiency. Innovations like MicroLED, intelligent brightness management, and automated adjustment enable displays to perform reliably under all lighting conditions, ensuring clear, comfortable, and long-lasting visual experiences. Users can expect brighter, smarter, and more efficient screens that meet both current and evolving brightness needs.
11. FAQS
Higher brightness requires more power. Outdoor screens with 5,000–10,000 nits consume more energy than indoor ones. Modern LEDs use efficient drivers to keep power use lower even at high brightness.
Yes. Built-in light sensors adjust brightness automatically—brighter under sunlight and dimmer at night—to save energy and protect the LEDs.
Larger screens viewed from farther away appear less bright. That’s why big outdoor displays need higher brightness than small indoor screens.
Quality LED screens keep about 70–80% of their brightness after 80,000–100,000 hours. Heat, humidity, and poor maintenance can speed up fading.
Yes. Too much brightness can wash out colors; too little makes them dull. Proper calibration keeps colors accurate and vibrant.
New tech like microLED and AI control will boost brightness efficiency—brighter images, lower power use, and longer lifespan.
12. Conclusion
Optimizing LED screen brightness is crucial for clear visuals, comfortable viewing, and long-term performance. By selecting the right brightness for the environment, monitoring uniformity, calibrating color and gray scale, and leveraging smart or automated adjustment technologies, users can maintain consistent luminance across all display types. Future advancements such as MicroLED and intelligent brightness management will further enhance visibility, energy efficiency, and overall display reliability. Understanding these principles ensures that LED screens deliver optimal brightness, whether for indoor signage, semi-outdoor spaces, or large-scale outdoor events.
For professional guidance or to choose the ideal LED screen brightness for your project, contact our experts today.
13. Recommend

IPS Display vs LED Display: 2026 Ultimate Comparison Guide
Compare IPS display vs LED displays to find the perfect screen for gaming, professional design, or retail. Explore 2026 updates on color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency to maximize your ROI.

QLED vs Crystal UHD: Which Display Fits Your Business ROI?
Compare QLED vs Crystal UHD for commercial displays. Learn which technology fits your budget, limits of LCD, and when to upgrade to seamless LED Video Walls.

How to Repair P6 Outdoor LED Display Sign Board Screen
Learning how to repair P6 outdoor LED display sign board screens requires expert knowledge. Discover our step-by-step guide on module replacement, waterproof sealing, and color calibration.
