Contact us
- Home
- »
- LED Display Technology
- »
- What Is Common Cathode LED Display Technology?
What is Common Cathode LED Display?
In the rapidly evolving world of digital signage, the demand for higher brightness and resolution often comes with a significant downside: excessive heat and power consumption. For system integrators and business owners, managing the operational costs of a massive outdoor billboard or a fine-pitch indoor video wall is just as important as the visual quality. This is where Common Cathode technology enters the conversation.
As a leading manufacturer of high-performance LED solutions, UnifyLED is committed to not just delivering screens, but delivering sustainable engineering. Common Cathode is no longer just a “buzzword”; it is the new standard for energy-saving display design. In this comprehensive guide, we will dismantle the physics behind the technology, explore the differences between the anode and cathode of led structures, and explain why this architecture is the future of the industry.
Table of Contents
1. Why Do Traditional LED Screens Overheat?
If you have ever stood close to a traditional outdoor LED billboard operating under the summer sun, you have likely felt the immense heat radiating from the surface. For years, the LED industry has battled two major enemies: high electricity bills and the risk of overheating. Traditional displays utilize a unified power supply method that, while functional, is incredibly inefficient. It forces the screen to consume more power than necessary, converting the excess energy directly into heat.
This heat does more than just raise the ambient temperature; it accelerates the degradation of the LED components, shifts colors (wavelength drift), and forces cooling fans to work overtime, creating noise and drawing even more power. To solve this, engineers re-imagined the fundamental power architecture of the LED module.
Enter Common Cathode LED display technology. By flipping the traditional power supply logic on its head, this technology promises to reduce power consumption by up to 50% while keeping the screen significantly cooler. For UnifyLED clients—whether they are installing digital billboards in the scorching Middle East or building silent, fanless conference rooms in Europe—understanding this technology is the key to maximizing Return on Investment (ROI) and ensuring long-term reliability.
2. What Are the Anode and Cathode of LED Components?
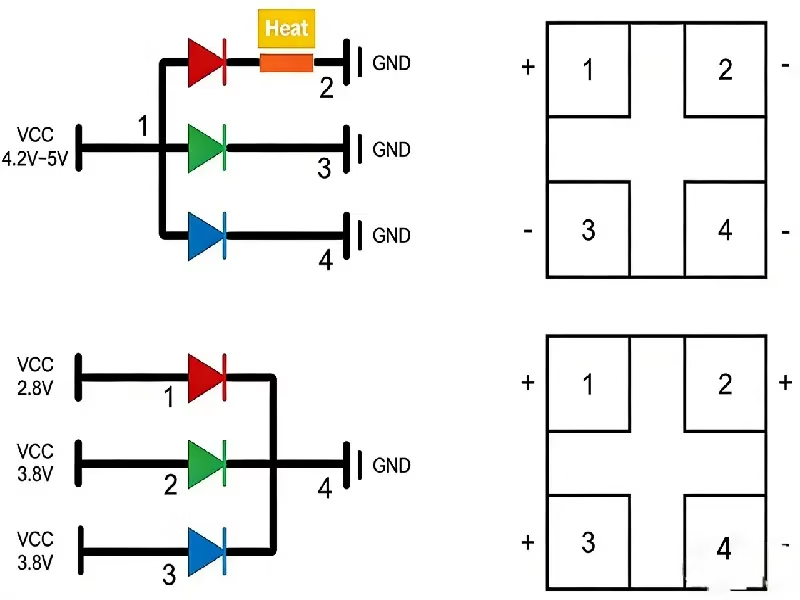
Before we can fully appreciate the advanced video wall technology, we must revisit the physics of the Light Emitting Diode (LED) itself. Every single pixel on a screen is made up of microscopic semiconductor chips. Crucially, the polarity of these chips matters. To make current flow and create light, we must understand the anode and cathode of led components.
An LED is a diode, which means current only flows in one direction. It has a positive electrode, known as the Anode, and a negative electrode, known as the Cathode. In a standard circuit, the current enters through the anode and exits through the cathode in led chips. The led cathode acts as the grounding point or the exit gate for the electrons.
In the context of display engineering, how we connect these electrodes determines the efficiency of the entire system. When you look at a raw LED bead, identifying the cathode of led is essential for circuit design. In traditional designs, the cathode was often just a passive return path. However, in modern “Common Cathode” designs, the cathode led connection becomes the star of the show, acting as the control point for the entire power management system. By manipulating how the cathode in led chips are grouped and powered, we can achieve remarkable gains in efficiency.
3. How Does LED RGB Common Cathode Technology Work?
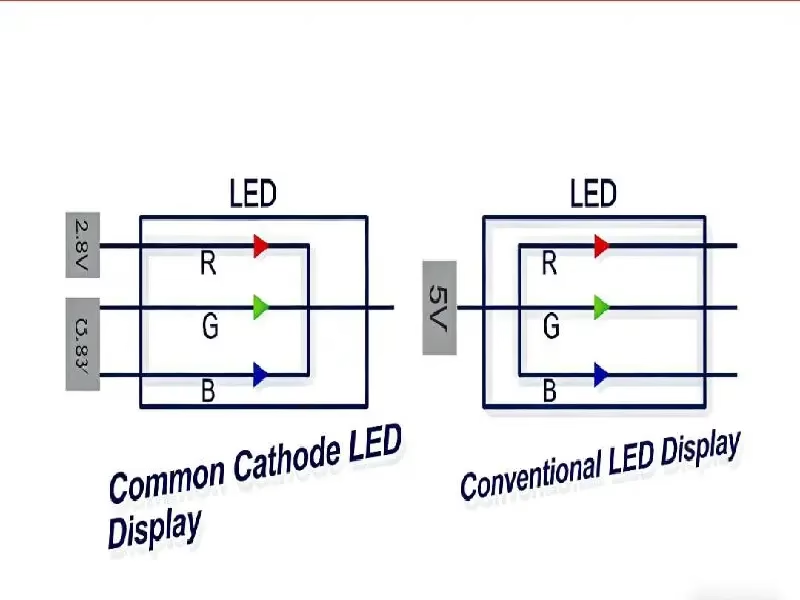
Common Cathode LED Display technology is an energy-saving power architecture where the current flows through the LED components to a shared negative terminal (cathode). Unlike traditional Common Anode systems that use a unified voltage, Common Cathode supplies precise, separate voltages to the Red, Green, and Blue chips (e.g., 2.8V for Red, 3.8V for Blue), reducing power consumption by up to 50% and significantly lowering heat generation.
The core mechanism lies in “Precision Power Supply.” An LED pixel creates white light by mixing Red, Green, and Blue (RGB) colors. The physics of these semiconductor materials dictates that they have different forward voltages to turn on:
Red chips typically require a lower voltage (approx. 2.8V).
Green and Blue chips require a higher voltage (approx. 3.8V).
In an led rgb common cathode system, the power supply is engineered to treat these chips differently. Instead of flooding the entire pixel with a single high voltage, the system splits the power rails. It delivers exactly 2.8V to the Red anode and 3.8V to the Green/Blue anodes. The current then flows through the chips and exits via the shared (common) negative terminal—hence the name “Common Cathode.”
This precise method ensures that the Red chip is not force-fed excess voltage that it doesn’t need, which is the primary source of inefficiency in older screens.
4. Common Cathode vs Anode: What Is the Key Difference?
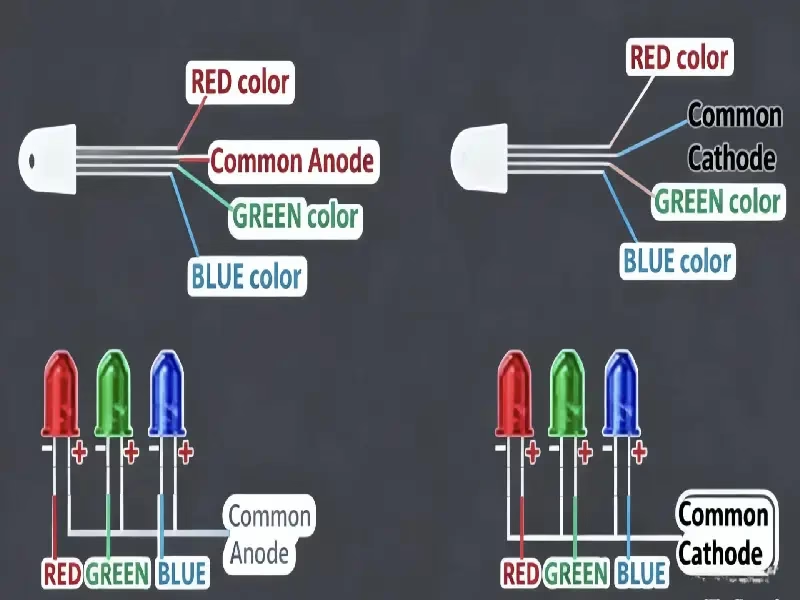
This is the most frequently asked question by buyers: Common Cathode vs Anode—which one should I choose and why?
The key difference is how they handle Voltage Drop (wasted energy).
In a traditional Common Anode display, the current flows from a shared positive terminal to the LEDs. The power supply provides a unified voltage (usually 3.8V or higher) to all chips to ensure the Blue and Green ones have enough power. But remember, the Red chip only needs 2.8V.
So, what happens to that extra 1V in a Common Anode screen? It is forced through a resistor and converted directly into heat.
Common Anode: Unified voltage = Wasted energy on Red chips = High Heat.
Common Cathode: Separate voltage = Zero waste = Cool Operation.
Comparison Table: Common Cathode vs Anode
| Feature | Common Anode (Traditional) | Common Cathode (Energy Saving) |
| Power Supply Mode | Unified Voltage (e.g., 3.8V for all) | Precise Voltage (2.8V Red, 3.8V Green/Blue) |
| Heat Generation | High (Excess voltage becomes heat) | Low (Cold Screen Technology) |
| Power Consumption | High | Reduced by 30% – 50% |
| Surface Temp | Hot to the touch | Cool (approx. 20°C lower) |
| Lifespan | Standard | Extended (Less thermal stress) |
When evaluating common cathode vs anode, think of it this way: Common Anode is like pouring the same amount of water into different-sized cups and letting the overflow spill. Common Cathode is pouring exactly the right amount into each cup, saving every drop.
5. Why Does the Cathode Common Design Save 50% Energy?
The energy-saving capabilities of cathode common technology are not marketing hype; they are based on electrical engineering principles. When we remove the need for a voltage-dropping resistor in the Red channel, the system becomes significantly more efficient.
In a typical scenario, a cathode common LED display can reduce power consumption by 30% to 50% compared to a standard Common Anode screen of the same brightness.
Let’s look at the math roughly. If a traditional P10 outdoor screen consumes 800 Watts per square meter on average, a Common Cathode version might only consume 450 to 500 Watts. For a massive 100-square-meter advertising billboard operating 18 hours a day, this translates to thousands of dollars saved in electricity bills annually.
Furthermore, because the screen generates less heat, the external cooling requirements drop. In many UnifyLED Common Cathode installations, clients find they no longer need heavy-duty air conditioning units behind the screen structure. This secondary saving (removing AC power costs) makes the cathode common approach the most financially sound choice for large-scale digital infrastructure.
6. Key Advantages of Common Cathode LED Displays
Beyond the electricity bill, adopting Common Cathode technology brings several technical advantages that enhance the visual performance and longevity of the display.
Lower Surface Temperature (Cold Screen):
Because the cathode in led design minimizes wasted energy, the screen surface temperature is typically 15°C to 20°C lower than traditional models. This is crucial for indoor touchable screens or outdoor screens where audiences are close by.Extended Lifespan:
Heat is the number one killer of electronic components. By operating at a cooler temperature, the LED chips and driver ICs experience less thermal stress. This significantly slows down the brightness attenuation (fading) of the LED lamps, potentially extending the screen’s life by 2-3 years.True Color Stability:
High temperatures can cause the wavelength of LED crystals to drift, leading to color distortion (e.g., white looking pinkish or bluish after hours of use). The stable, cool operation of LED RGB common cathode technology ensures that the colors remain true and vibrant, even after 24/7 operation.Lower Failure Rate:
The precision power supply reduces the likelihood of short circuits and component burnout, making UnifyLED screens more reliable for critical missions.
Why Lower Temperature Extends the Cathode LED Lifespan
Heat is the enemy of electronics. High temperatures cause LED crystals to degrade and dim faster. By maintaining a surface temperature that is approx. 20°C cooler than traditional models, the cathode led components experience far less thermal stress.
This means:
Slower Attenuation: Your screen stays brighter for more years.
Color Stability: No wavelength drift (preventing the screen from looking pinkish or bluish over time).
Reliability: The failure rate of driver ICs drops significantly when they aren’t overheating.
7. Where and When Should You Deploy Common Cathode Displays?
While Common Cathode technology involves a slightly higher initial manufacturing cost due to specialized driver ICs, it is the superior choice for high-value scenarios. At UnifyLED, we integrate this tech into our premium solutions:
1. Outdoor Fixed LED Displays:
Especially in regions with high ambient temperatures (like the Middle East, Arizona, or Australia). A Common Cathode screen ensures the display doesn’t overheat even under direct sunlight.
2. Fine Pixel Pitch Indoor Video Walls:
For pixel pitches below P1.5, LEDs are packed densely. Traditional screens would become hot to the touch. Common Cathode technology allows for silent, fanless operation—perfect for TV studios and conference rooms.
Pro Tip: Check out our [Aluminum Cabinet Series], which combines robust materials with Common Cathode tech for the ultimate durability.
8. FAQs about Common Cathode Technology
The main difference lies in the power supply direction and precision. Common Cathode vs Anode boils down to efficiency: Common Cathode supplies separate, precise voltages to Red, Green, and Blue chips, whereas Common Anode supplies a single, unified voltage that wastes energy as heat.
Yes, in the cathode of led circuit topology, the current flows through the LED and exits via the cathode, which connects to the ground (negative) terminal of the driver IC.
It is called "Common" because the cathode led terminals of the RGB chips are connected to a shared negative line, while the anodes are powered independently.
9. Summary
The shift from Common Anode to Common Cathode represents a maturation in the LED display industry. We are moving away from brute-force brightness towards intelligent, sustainable, and precision-engineered visual solutions.
By understanding the role of the cathode in led technology and the efficiency of the led rgb common cathode architecture, buyers can make smarter investment decisions. You are not just buying a screen; you are buying lower electricity bills, a longer operational lifespan, and a superior visual experience.
UnifyLED has integrated Common Cathode technology into our premium outdoor and indoor product lines, including our energy-saving aluminum series. If you are ready to upgrade to a display that pays for itself through energy savings, contact our engineering team today.
Reference:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seven-segment_display
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light-emitting_diode#Colors_and_materials
10. Recommend

IPS Display vs LED Display: 2026 Ultimate Comparison Guide
Compare IPS display vs LED displays to find the perfect screen for gaming, professional design, or retail. Explore 2026 updates on color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency to maximize your ROI.

QLED vs Crystal UHD: Which Display Fits Your Business ROI?
Compare QLED vs Crystal UHD for commercial displays. Learn which technology fits your budget, limits of LCD, and when to upgrade to seamless LED Video Walls.

How to Repair P6 Outdoor LED Display Sign Board Screen
Learning how to repair P6 outdoor LED display sign board screens requires expert knowledge. Discover our step-by-step guide on module replacement, waterproof sealing, and color calibration.
