- Home
- »
- LED Display Technology
- »
- LED Packaging Technology Guide: SMD vs COB vs GOB vs MIP
LED Packaging Technology Guide: SMD vs COB vs GOB vs MIP
Table of Contents
LED packaging technology defines how LED chips are assembled, protected, and connected within display modules and lighting products. It directly impacts brightness, color accuracy, viewing angles, heat dissipation, and the overall lifespan of LED devices.
Today’s LED displays rely on multiple packaging methods, including SMD (Surface Mounted Device), IMD (Integrated Matrix Device), COB (Chip on Board), and GOB (Glue on Board). Each technology offers unique advantages and challenges for applications ranging from indoor fine-pitch screens to outdoor high-brightness displays.
Understanding LED packaging technology is essential for manufacturers, designers, and buyers to choose the right solution for performance, durability, and maintenance efficiency. This guide explores current packaging types, compares their features, and highlights future trends, including Mini and Micro LED innovations.
1. What Is LED Packaging Technology?
LED packaging technology refers to the methods and processes used to assemble, protect, and connect individual LED chips into functional display modules or lighting units. This technology directly affects brightness, color consistency, viewing angles, heat dissipation, and the overall lifespan of LED devices worldwide. From indoor fine-pitch displays in offices to massive outdoor billboards and stadium screens, packaging determines whether an LED module performs reliably under real-world conditions.
The primary functions of LED packaging include:
Protection: Encapsulation materials such as epoxy, transparent resins, or advanced polymers shield the LED chip from environmental damage, including moisture, dust, UV exposure, and mechanical stress. This ensures the display maintains consistent brightness and color quality even in challenging outdoor or high-traffic environments.
Electrical Connection: Packaging establishes secure pathways between the LED chip and the module’s circuitry, enabling stable current flow, preventing short circuits, and supporting reliable operation over time.
Heat Management: Efficient packaging dissipates heat generated during operation, preventing performance degradation and extending the LED’s operational life, which is critical for high-brightness and long-duration applications.
Optical Performance: The design of the packaging affects brightness, contrast, viewing angles, and color uniformity, ensuring that both indoor and outdoor displays meet precise visual requirements.
Over the past decade, several packaging methods—including SMD (Surface Mounted Device), IMD (Integrated Matrix Device), COB (Chip on Board), and GOB (Glue on Board)—have dominated global LED display production. Each technology offers distinct advantages and trade-offs in terms of cost, maintenance, and performance. Furthermore, next-generation packaging approaches like Mini LED and Micro LED are gaining traction for applications requiring ultra-fine pixel pitch, higher energy efficiency, and enhanced durability.
Understanding LED packaging technology is essential for manufacturers, engineers, and buyers. It enables informed decisions when selecting modules, balancing performance, cost, and maintenance needs. By mastering these fundamentals, users can confidently choose the right technology for indoor commercial screens, outdoor high-brightness displays, or interactive LED installations.
Next, we will explore the main LED packaging types today, their unique features, and the advantages and limitations of each.
2. Main LED Packaging Technology Types
LED packaging technology has evolved significantly over the years to meet different performance, cost, and application requirements. Today, four main packaging types dominate the global LED display industry: SMD (Surface Mounted Device), IMD (Integrated Matrix Device), COB (Chip on Board), and GOB (Glue on Board). Each type offers unique advantages and trade-offs.
SMD – Surface Mounted Device


How it works:
SMD packaging mounts one or more LED chips directly onto a substrate. The chips are encapsulated with protective resin, and electrical connections are soldered to the substrate leads. Typically, an SMD unit contains red, green, and blue chips in a single pixel.
Advantages:
Mature, cost-effective, and widely available
Flexible module design and easy assembly
Good brightness and wide viewing angles
Easy maintenance; individual units can be replaced
Limitations:
Pixel pitch below 1.2mm is challenging
Moderate protection against harsh outdoor environments
Heat dissipation requires careful design for larger panels
Applications:
Indoor commercial displays, retail screens
Outdoor advertising and billboards
Rental LED screens for events
IMD – Integrated Matrix Device (4-in-1)
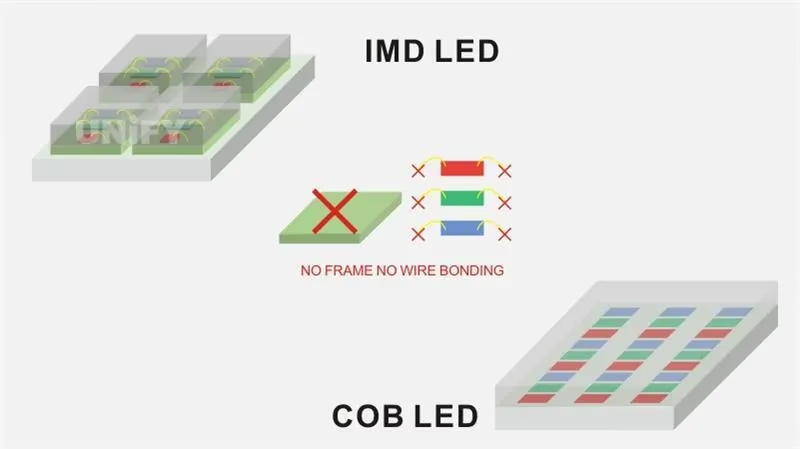
How it works:
IMD, or “four-in-one” packaging, integrates four pixels into a single package. It inherits SMD technology but increases pixel density and uniformity, making it ideal for fine-pitch Mini LED applications.
Advantages:
Higher brightness and improved uniformity
Compact, high-integration design
Easier maintenance than conventional multi-chip SMD units
Lower risk of color deviation and light leakage
Limitations:
Slightly higher production cost
Requires precise assembly and calibration
Applications:
Fine-pitch LED displays
Small pixel pitch LED panels for commercial or interactive screens
COB – Chip on Board


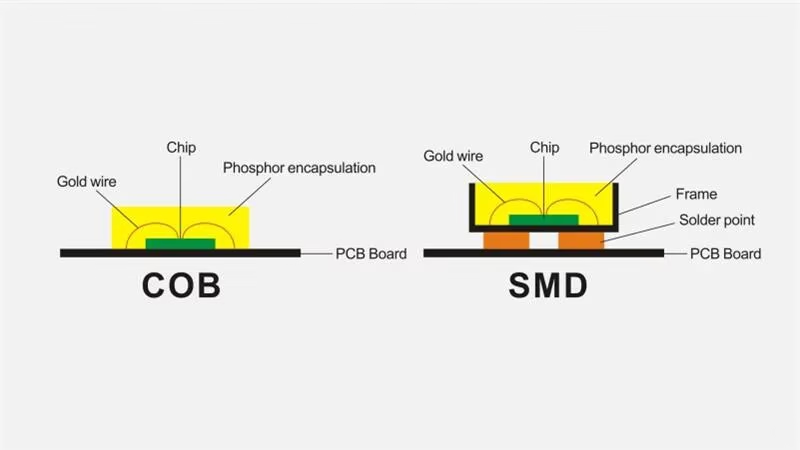


How it works:
COB packaging mounts bare LED chips directly on a substrate without leads. After bonding, chips are encapsulated with resin, forming a uniform light-emitting surface.
Advantages:
Enables very fine pixel pitch, even <1mm
Uniform light output, reducing Moiré effects
Higher brightness per unit area
COB technology offers better heat dissipation compared to traditional SMD, which can contribute to optimizing your LED display power consumption.
Limitations:
Difficult maintenance; chips are not individually replaceable
Lower production yield and higher cost
Requires careful heat management
Applications:
High-end indoor fine-pitch LED displays
Applications where pixel density and uniformity are critical
GOB – Glue on Board

How it works:
GOB is an advanced method where a transparent protective material covers the LED module, including the substrate and chips. This layer provides mechanical protection and environmental resistance.
Advantages:
Anti-dust, waterproof, moisture-proof, anti-UV, and shock-resistant
Flat and uniform light surface improves brightness and viewing angles
Reduces glare and visual fatigue, suitable for human-interactive displays
Retains SMD/COB advantages while addressing original limitations
Limitations:
Slightly more complex production than standard SMD
Repair may be moderately difficult but easier than COB
Applications:
Commercial LED displays and small-pitch interactive screens
Indoor fine-pitch panels in shopping malls, airports, and control rooms
SMD, IMD, COB, and GOB each have distinct strengths: SMD offers flexibility and cost-effectiveness, IMD enhances fine-pitch uniformity, COB delivers ultra-fine pixel density, and GOB ensures durability with flat light surfaces. Together, they cover most indoor, outdoor, and commercial LED display needs.
3. Next-Gen LED Packaging Technology
As LED technology advances, next-generation packaging methods like EMC, Flip-Chip, and Mini/Micro LED are emerging to meet demands for higher pixel density, energy efficiency, and superior visual performance.
EMC (Epoxy Molding Compound): Primarily used in industrial and outdoor applications where durability and heat management are critical. It offers strong mechanical protection but remains a niche technology due to higher costs and precise manufacturing requirements.
Flip-Chip: Gradually adopted in high-end indoor and fine-pitch displays, as well as automotive displays. It provides excellent heat dissipation, higher brightness, and allows smaller pixel pitches, but production is more complex and costly.
Mini/Micro LED: Rapidly gaining traction in premium TVs, interactive commercial screens, and AR/VR devices. Offers ultra-fine pixels, high brightness, wide color gamut, and superior contrast. Challenges include high manufacturing precision, high cost, and limited mass production, especially for Micro LED.
These technologies represent the future of LED packaging, with Mini/Micro LED showing the most growth potential, while EMC and Flip-Chip remain specialized solutions for targeted applications.
4. FAQs about LED Packaging Technology
SMD is flexible and cost-effective, COB allows ultra-fine pixels, and GOB adds durability with flat light surfaces.
COB and IMD are ideal for fine pixels; GOB works well for interactive commercial displays. SMD is less suitable below 1.2mm.
IMD and COB provide uniform brightness and color, while GOB ensures flat light emission and reduces glare.
SMD and GOB are suitable for both indoor and outdoor; COB is mostly used indoors for high-resolution displays. GOB adds extra protection for harsh environments.
GOB and EMC improve durability and reduce maintenance needs. COB is harder to repair, while SMD and IMD are easier to service. Proper heat management extends LED screen lifespan.
SMD is most cost-effective, IMD slightly higher, COB and GOB higher due to precision and protection features. Next-gen Mini/Micro LED are premium options with higher manufacturing costs.
Technologies like EMC, Flip-Chip, and Mini/Micro LED focus on finer pixel pitch, higher brightness, better heat management, and energy efficiency for premium and industrial applications.
5. Conclusion
Choosing the right LED packaging technology goes beyond just SMD, COB, or GOB. It determines the display’s brightness, color accuracy, lifespan, and suitability for indoor, outdoor, or interactive applications. Understanding each type’s strengths and limitations helps LED screen manufacturers and buyers make smarter decisions and future-proof their LED installations.
6. Recommend

IPS Display vs LED Display: 2026 Ultimate Comparison Guide
Compare IPS display vs LED displays to find the perfect screen for gaming, professional design, or retail. Explore 2026 updates on color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency to maximize your ROI.

QLED vs Crystal UHD: Which Display Fits Your Business ROI?
Compare QLED vs Crystal UHD for commercial displays. Learn which technology fits your budget, limits of LCD, and when to upgrade to seamless LED Video Walls.

How to Repair P6 Outdoor LED Display Sign Board Screen
Learning how to repair P6 outdoor LED display sign board screens requires expert knowledge. Discover our step-by-step guide on module replacement, waterproof sealing, and color calibration.
